Chapter 8 Lab assays to monitor immune response
In order to assess the systemic and the mucosal immune response of the Nile tilapia during our experiment, three different assays will be used. Those assays will allow us to demonstrate that there is indeed an effect of the vaccines on immune response in the animals. The three assays will help to quantify this effect by measuring the activation of the main components of the adaptive/humoral immune system and their kinetics (the activity over time).
8.1 ELISA for IgM and IgT
ELISA is an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay “for the presence of antibodies, antigens,” proteins and glycoproteins in biological samples. ELISA technique is widely used for rapid diagnostic tests such as the diagnosis of HIV infection, pregnancy tests or the detection of food allergens. The principle of this technique is based on the use of an enzyme conjugated to an antibody which by reacting with a colorless substrate gives a colored reaction product and which is therefore detectable. This is called a chromogenic substrate. Different enzymes are used for ELISA tests including alkaline phosphatase, horseradish peroxidase (HRP) or beta-galactosidase. The ELISA assay will provide informations on the Ab titer of the fish, IgM and IgT respectively are targets in the assay.
8.2 PCR of key immune genes
Real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is a laboratory technique using 1) reverse-transcription (RNA into DNA) (in this context called complementary DNA or cDNA) and 2) amplification of specific DNA targets using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) (Freeman et al.,1999). It is primarily used to measure the amount of a specific RNA. This is achieved by monitoring the amplification reaction using fluorescence, a technique called real-time PCR or quantitative PCR (qPCR). Combined RT-PCR and qPCR are routinely used for analysis of gene expression and quantification of viral RNA in research and clinical settings.
8.2.1 Normalization of gene expression for RT-PCR
Choosing the suitable reference gene is critical for normalizing target genes expression in qPCR. Wang et al. (2015) selected for O.niloticus, six commonly used endogenous controls as candidate reference genes to evaluate and analyze their expression levels, stabilities and normalization to the immune-related gene IgM expression during vaccination and infection in spleen of tilapia with RefFinder and GeNorm programs with very good results. The six reference genes for RT-PCR of O.niloticus are genes ubiquitously and constitutively expressed in the animal. They are also well known as “house-keeping” genes/mRNAs. (see below).
Insert table
8.3 Agglutination test
8.3.1 Qualitative detection of the presence of antibodies by agglutination
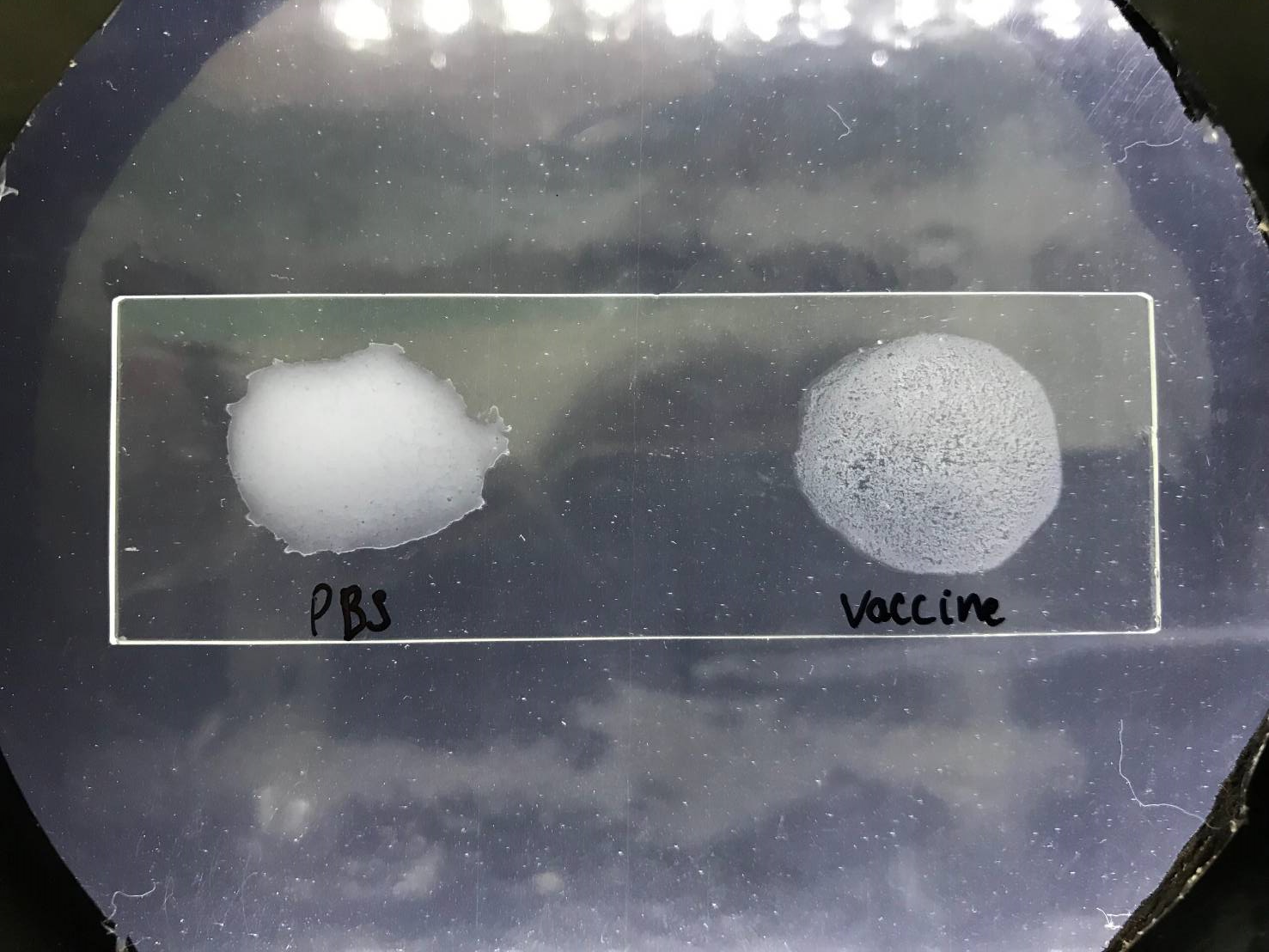

Figure 8.1: Agglutination test on a blade - Qualitative antibody agglutination test with the antigen: A sample from fish containing antibodies istested against a specific antigen. Credits: Ha Thanh Dong
8.3.2 Quantitative antibody agglutination titration
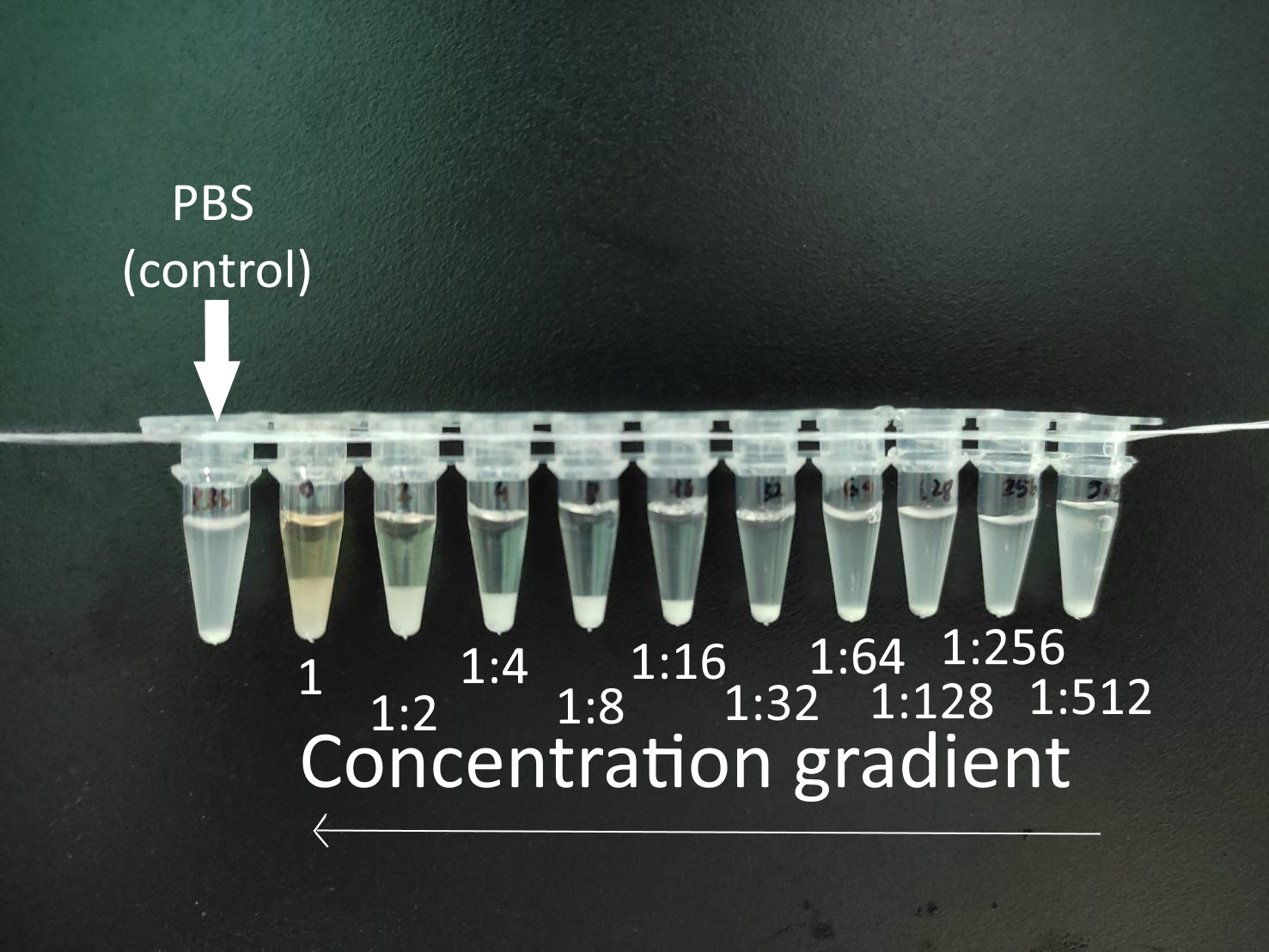
Figure 8.2: Quantitative agglutination test with serial dilutions - A sample obtained from the fish after immunization is tested against PBS (control (Ct)) or against the specific agglutinating Ag at different serial dilutions. Credits: Ha Thanh Dong